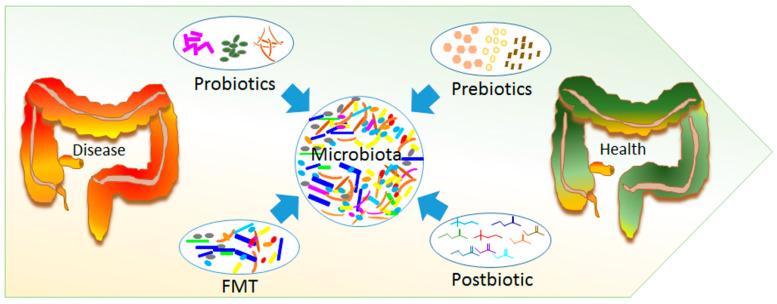
The gut microbiome is the collection of all the microbes that live in the gastrointestinal tract. These microbes play an important role in human health, including digestion, metabolism, and immunity. The composition of the gut microbiome varies between individuals and is influenced by diet, age, and lifestyle factors. There is growing evidence that fermented food can positively impact health. Fermented food is a rich source of probiotics, which are live microorganisms that provide health benefits when consumed. Probiotics are thought to promote gut health by helping maintain the balance of gut microbes and supporting the immune system. They may also help to regulate metabolism and reduce inflammation. In addition to probiotics, fermented food also contains other beneficial compounds, such as enzymes, vitamins, and minerals. These compounds support gut health and contribute to the overall nutritional value of fermented foods.
Diet is a major source of precursors for metabolite production, and the microbiome plays a central role in host metabolism. Fermented food is a particularly important source of nutrients for the microbiome, as it provides probiotics and other beneficial compounds that support gut health. The microbiome is also involved in the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which are important for maintaining gut health and regulating metabolism. SCFAs are thought to play a role in obesity and other metabolic disorders, and manipulating the microbiome through diet may be a potential therapeutic strategy for these conditions.
Fermented food has been shown to have a number of health benefits, including improved digestion, increased nutrient absorption, and enhanced immune function. Fermented food is also a good source of antioxidants, which can help to protect against cell damage and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. The health benefits of fermented food are thought to be due to the unique combination of beneficial compounds that are present in these foods. These compounds work together to support gut health and promote a healthy metabolism. The microbiota is a collection of microbes that live in the gut and play a role in digestion, metabolism, and immunity. Fermented food contains beneficial bacteria that can help to maintain a healthy microbiome and support the immune system.
A diet rich in fermented food may be a helpful strategy for preventing or treating obesity and other metabolic disorders. The probiotics and other beneficial compounds in fermented food can help to regulate metabolism and reduce inflammation. Manipulating the microbiome through diet may be a potential therapeutic strategy for these conditions. Fermented food is a rich source of nutrients that support gut health and contribute to the overall nutritional value of the diet. Including fermented food in the diet may be a helpful strategy for preventing or treating obesity and other metabolic disorders.
In addition to providing nutrients, the microbiome also plays a role in the elimination of toxins from the body. The gut microbiome is responsible for breaking down and excreting many of the toxins we are exposed to daily, including those found in food and the environment. This process is known as biotransformation, an important function of the microbiome that helps keep us healthy. The microbiome is a complex and dynamic ecosystem that is constantly changing in response to our diet and environment. By understanding how the microbiome affects metabolism, we may be able to develop new dietary and therapeutic strategies to support gut health and optimize metabolism.